Healthwise
Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein.
Female Genital Problems and Injuries
Overview
It's common to have minor vaginal problems from time to time. These problems can be related to menstrual cycles, sex, infection, and birth control methods. They also can be related to hormone changes, medicines, or changes after pregnancy.
A change in your normal vaginal discharge may be the first sign of a vaginal problem. Changes in urination also may be a symptom of a problem. These changes may include having to urinate more often or having a burning feeling when you urinate.
Conditions that may cause a change in your normal vaginal discharge include:
- Infections of the vagina. These may include a yeast infection, trichomoniasis, human papillomavirus (HPV), or herpes.
- Infection of the cervix (cervicitis).
- An object in the vagina. An example is a forgotten tampon.
- Bacterial vaginosis
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Examples are chlamydia or gonorrhea.
- Vaginal medicines or douching.
Pelvic pain
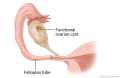
The exact cause of pelvic pain may be hard to find. How severe your pain is and what other symptoms you have may help find out what is causing the pain. For example, a condition such as functional ovarian cysts may cause pelvic pain and vaginal bleeding when you aren't having your period.
Vaginal infections
If you think you may have symptoms of an STI:
- Do not have sexual contact while you wait for an appointment. This will prevent the spread of the infection.
- Do not douche. It changes the normal balance of bacteria in the vagina. Douching may flush an infection up into your uterus or fallopian tubes and cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
An infection may occur when there is a change in the normal balance of organisms in your vagina. The excess growth of yeast cells or bacteria can cause a vaginal infection. Viruses can also cause a vaginal infection.
Common symptoms of a vaginal infection include:
- Increase or change in the vaginal discharge. The discharge may be gray, green, or yellow.
- Vaginal redness, swelling, itching, or pain.
- Vaginal odor.
- Burning with urination.
- Pain or bleeding with sex.
If you are pregnant and have vaginal symptoms, talk with your doctor about your symptoms. Do this before you consider any home treatment. Some home treatments may not work, depending on the cause of your infection. Certain infections can affect your pregnancy. So it is important to talk with your doctor and be treated in the right way.
Vaginal infections may increase the risk for pelvic infections, such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
Vaginal or vulvar problems
Other vaginal or vulvar problems may occur from the use of birth control methods, the use of medicines, or changes in hormones, or as a result of changes after pregnancy. These problems include:
- Vaginal prolapse. This may cause urination and bowel changes.
- Retained tampon, birth control device, or foreign object.
- Vulvar or vaginal injury.
- Vulvar pain (vulvodynia).
- Pudendal neuralgia. This can happen from pressure on the pudendal nerve in the genital area, especially when sitting.
- Noninfectious vaginitis. Examples of this include:
- An allergic reaction or irritation from chemicals. Examples are those found in vaginal sprays, douches, or spermicides.
- Hormone changes related to menopause. An example is atrophic vaginitis.
- Use of antibiotics and other medicines. These may change the balance of organisms in the vagina.
A young child with unusual vaginal symptoms should be checked by the doctor to find the cause. Vaginitis in a young child may be caused by:
- A piece of toilet paper in the vagina.
- Bacteria that have spread from the anus to the vagina.
- The spread by the hands to the vagina of bacteria from an upper respiratory infection of the ears (otitis media) or throat (tonsillitis).
A young child with vaginal symptoms must also be checked for possible sexual abuse.
Rashes, sores, blisters, or lumps in the vaginal or vulvar area
Many conditions can cause a rash, sore, blister, or lump in your vagina or vulva. One of the most common causes of a rash is genital skin irritation. This may occur when soap is not rinsed off the skin or when tight-fitting or wet clothes rub against the skin. A sore, blister, or lump in your vagina or vulva may require a visit to your doctor.
Check Your Symptoms
The medical assessment of symptoms is based on the body parts you have.
- If you are transgender or nonbinary, choose the sex that matches the body parts (such as ovaries, testes, prostate, breasts, penis, or vagina) you now have in the area where you are having symptoms.
- If your symptoms aren’t related to those organs, you can choose the gender you identify with.
- If you have some organs of both sexes, you may need to go through this triage tool twice (once as "male" and once as "female"). This will make sure that the tool asks the right questions for you.
Many things can affect how your body responds to a symptom and what kind of care you may need. These include:
- Your age. Babies and older adults tend to get sicker quicker.
- Your overall health. If you have a condition such as diabetes, HIV, cancer, or heart disease, you may need to pay closer attention to certain symptoms and seek care sooner.
- Medicines you take. Certain medicines, such as blood thinners (anticoagulants), medicines that suppress the immune system like steroids or chemotherapy, herbal remedies, or supplements can cause symptoms or make them worse.
- Recent health events, such as surgery or injury. These kinds of events can cause symptoms afterwards or make them more serious.
- Your health habits and lifestyle, such as eating and exercise habits, smoking, alcohol or drug use, sexual history, and travel.
Try Home Treatment
You have answered all the questions. Based on your answers, you may be able to take care of this problem at home.
- Try home treatment to relieve the symptoms.
- Call your doctor if symptoms get worse or you have any concerns (for example, if symptoms are not getting better as you would expect). You may need care sooner.
Urinary symptoms may include:
- Pain when you urinate.
- Trouble urinating.
- Not being able to urinate at all.
- Blood in your urine.
Symptoms of a vaginal infection may include:
- Vaginal itching.
- Vaginal discharge that is not normal for you.
- Red, irritated skin in the vaginal area.
- Pain when you urinate.
- Pain or bleeding when you have sex.
Many prescription and nonprescription medicines can cause vaginal symptoms. A few examples are:
- Antibiotics.
- Birth control pills.
- Hormone therapy.
- Chemotherapy for cancer.
- Vaginal sprays, douches, and spermicides.
Pain in adults and older children
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that you can't stand it for more than a few hours, can't sleep, and can't do anything else except focus on the pain.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The pain is bad enough to disrupt your normal activities and your sleep, but you can tolerate it for hours or days. Moderate can also mean pain that comes and goes even if it's severe when it's there.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): You notice the pain, but it is not bad enough to disrupt your sleep or activities.
Pain in children under 3 years
It can be hard to tell how much pain a baby or toddler is in.
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that the baby cannot sleep, cannot get comfortable, and cries constantly no matter what you do. The baby may kick, make fists, or grimace.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The baby is very fussy, clings to you a lot, and may have trouble sleeping but responds when you try to comfort him or her.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): The baby is a little fussy and clings to you a little but responds when you try to comfort him or her.
Seek Care Now
Based on your answers, you may need care right away. The problem is likely to get worse without medical care.
- Call your doctor now to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or you don't have one, seek care in the next hour.
- You do not need to call an ambulance unless:
- You cannot travel safely either by driving yourself or by having someone else drive you.
- You are in an area where heavy traffic or other problems may slow you down.
Seek Care Today
Based on your answers, you may need care soon. The problem probably will not get better without medical care.
- Call your doctor or telehealth provider today to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or telehealth provider or you don't have one, seek care today.
- If it is evening, watch the symptoms and seek care in the morning.
- If the symptoms get worse, seek care sooner.
What are your options for medical care?
Today your options for where to get your medical care are greater than ever before. You may not even have to leave your home to get the care you want and need. You can choose based on what your health problem is and what works best for you.
- Telehealth is a video call with a health care provider. It can be a convenient way to get medical advice or treatment. Some insurers provide access to telehealth that may be available 24 hours a day. Telehealth for less serious problems may cost less and be faster than in-person clinic visits.
- Urgent care and retail clinics are options if you don't have a doctor, you can't or don't want to wait to see your own doctor, or a telehealth visit can’t treat the problem.
- Virtual care from your primary provider or a telehealth service can be delivered through your smartphone, computer, or tablet.
Make an Appointment
Based on your answers, the problem may not improve without medical care.
- Make an appointment to see your doctor in the next 1 to 2 weeks, or contact your telehealth provider.
- If appropriate, try home treatment while you are waiting for the appointment.
- If symptoms get worse or you have any concerns, call your doctor or telehealth provider. You may need care sooner.
What are your options for medical care?
Today your options for where to get your medical care are greater than ever before. You may not even have to leave your home to get the care you want and need. You can choose based on what your health problem is and what works best for you.
- Telehealth is a video call with a health care provider. It can be a convenient way to get medical advice or treatment. Some insurers provide access to telehealth that may be available 24 hours a day. Telehealth for less serious problems may cost less and be faster than in-person clinic visits.
- Urgent care and retail clinics are options if you don't have a doctor, you can't or don't want to wait to see your own doctor, or a telehealth visit can’t treat the problem.
- Virtual care from your primary provider or a telehealth service can be delivered through your smartphone, computer, or tablet.
Self-Care
A vaginal infection may clear up without treatment in a few days.
If you could be pregnant, do a home pregnancy test. Anyone with abnormal vaginal symptoms should talk with a doctor about these symptoms before using any home treatment or nonprescription medicines. Try the following tips to help care for a vaginal infection.
- Avoid sex when you have symptoms.
This will help irritated vaginal tissues heal. When you have sex again, try using a vaginal lubricant, such as Astroglide, to reduce irritation caused by having sex.
- Do not scratch the vagina or vulva.
Relieve itching with a cold water compress or cool baths. Warm baths may also relieve pain and itching.
- Check for an object in the vagina.
Make sure that the cause of your symptoms is not a forgotten tampon or other foreign object that needs to be removed.
- Wear loose-fitting, cotton clothing.
Stay away from nylon and synthetics, because they hold heat and moisture close to the skin. This makes it easier for an infection to start. You may want to remove pajama bottoms or underwear when you sleep.
- Don't douche or use powders, sprays, or perfumes in your vagina or on your vulva.
These items can change the normal balance of organisms in your vagina.
Recurrent vaginal yeast infection
If you have symptoms of a vaginal yeast infection and have been diagnosed and treated by your doctor for this in the past, you may want to try treating it at home. You can use an over-the-counter medicine to treat your symptoms. Examples of medicines are tioconazole (Vagistat), clotrimazole (Gyne-Lotrimin), and miconazole (Monistat).
If your symptoms don't improve with home treatment, contact your doctor. Vaginal symptoms that may be related to another type of vaginal infection or a cervical infection need to be checked.
If you are pregnant or if you take the blood-thinning medicine warfarin, talk to your doctor before using an over-the-counter medicine for a yeast infection. If you take warfarin and use an over-the-counter medicine, you may have increased bruising and abnormal bleeding.
When to call for help during self-care
Call a doctor if any of the following occur during self-care at home:
- New symptoms of a vaginal infection.
- New vaginal bleeding.
- New fever or pain.
- Symptoms occur more often or are more severe.
Preparing For Your Appointment
You can help your doctor diagnose and treat your condition by being prepared for your appointment.
Related Information
Credits
Current as of: April 30, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: April 30, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content.
To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com.
© 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.